The Top 10 Skills Every Data Scientist Needs to Succeed
-
Any Must Have Skills for Data Scientists?
-
Requires Technical Skills
-
Mastering Programming Languages
-
Statistical Proficiency
-
Machine Learning Expertise
-
Data Visualization Mastery
-
Database Management Skills
-
Requires Non-Technical Skills
-
Problem-Solving Skills
-
Communication Skills
-
Business Acumen
-
Curiosity and Continuous Learning
-
Teamwork and Collaboration
-
How to Gain Important Data Science Skills
-
Make Use of Internet Resources
-
Online Courses
-
FAQ's

Over the past years, data science has taken center stage as a coveted industry, calling for proficient individuals who possess the ability to decrypt and unravel complex data sets. Excelling in this fiercely competitive field requires a dynamic skill set, encompassing technical expertise, keen analytical aptitude, and strong communication process.
In this insightful piece, we will delve into the top ten skills that data scientists must possess to reach their full potential, backed by compelling data and expert opinions.
Any Must Have Skills for Data Scientists?
Yes. The ability to gather, process, and present data skills are required for becoming a data scientist. Technical expertise in fields like programming, database administration, advanced mathematics, and data visualization is required for this. Soft skills like public speaking and teamwork are also essential for success in this sector.
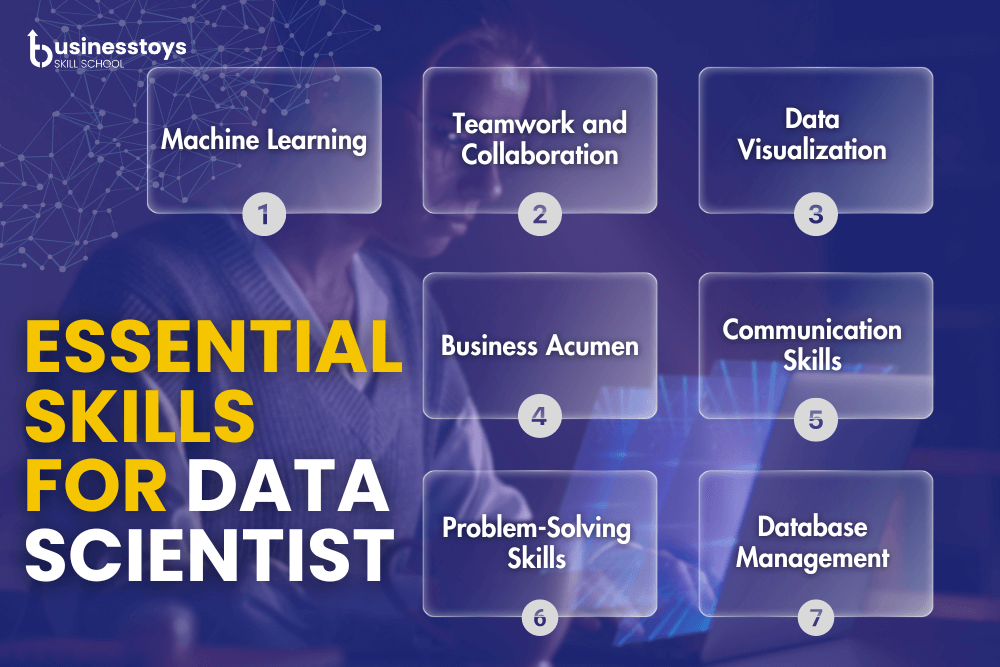
Requires Technical Skills
For data scientists to succeed in their jobs, a variety of technical skills are necessary. A data scientist has to possess the following critical technical skills:
- • Programming
- • Statistical
- • Machine Learning
- • Data Visualization
- • Database Management
Mastering Programming Languages
To excel in data science, mastering programming languages such as Python, R, and SQL is essential. These powerful tools are the driving force behind data science, empowering experts to effectively handle and study immense amounts of data. Elevating your coding proficiency is instrumental in unleashing the immense possibilities of data science.
Statistical Proficiency
Becoming proficient in statistical concepts and mathematical techniques is essential for data scientists. By comprehending these concepts, one can uncover valuable insights, make well-informed choices, and construct resilient models that can withstand real-world hurdles.
Machine Learning Expertise
To become a skilled data scientist, one must first master the nuances of machine learning. It's a powerful technique that not only enhances the efficiency of data analysis and prediction, but also expands your capabilities as a data scientist. While basic methods like linear regression enable the forecasting of future outcomes, delving into advanced models like Random Forest grants you a wider range of skill and expertise.
Data Visualization Mastery
Data scientists frequently handle intricate data sets that demand an engaging and comprehensible format for presentation. Translate complex findings into compelling narratives through data visualization. Tools like Tableau and Power BI can help you create visually appealing representations of data, making it easier for stakeholders to comprehend and act upon your insights.
Database Management Skills
Being able to oversee and gather information from databases is a critical skill. Proficiency in SQL and other database management systems is essential for efficiently retrieving relevant data.

Requires Non-Technical Skills
Although technical knowledge is necessary for a data scientist, non-technical skills are also necessary to succeed in the industry. The following are essential non-technical skills for a data scientist:
- • Problem-Solving Skills
- • Communication Skills
- • Business Acumen
- • Curiosity and Continuous Learning
- • Teamwork and Collaboration
Problem-Solving Skills
Data scientists are continually faced with complex challenges that require sharp analytical skills and logical reasoning. The ability to dissect problems into smaller components and formulate creative solutions is crucial.
Communication Skills
Effective communication skills are a crucial asset for data scientists. They must be able to convey their findings and recommendations to both technical and non-technical stakeholders with fluency and engagement. This includes presenting complex information in a clear and concise manner. By effectively communicating technical information to non-technical stakeholders, data scientists promote collaboration and ensure that their insights drive informed decision-making at all levels of an organization.
Business Acumen
To become highly skilled data scientists, mastering the fundamental business objectives and aligning key data findings with organizational aims is essential. Successful data experts possess the aptitude to identify opportunities to leverage data for business success and proficiently convey technical discoveries to actionable strategies. In order to bridge the gap between technical proficiency and business goals, data scientists must cultivate solid business acumen. By doing so, they can effectively align data-driven insights with organizational objectives, ultimately amplifying the impact of their analyses.
Curiosity and Continuous Learning
The ever-changing landscape of data science is a whirlwind of dynamic advancements, with new algorithms, tools, and techniques emerging consistently. To succeed in this fast-paced realm, data scientists must possess a relentless thirst for knowledge and a constant drive for ongoing education. Keeping up with the latest developments in data science is of utmost importance in order to stay ahead in this fiercely competitive field.
Teamwork and Collaboration
Data science projects often involve collaboration with cross-functional teams. Being able to work effectively with others, share insights, and integrate feedback is vital for success.
How to Gain Important Data Science Skills
It is never easy to build new talents; understanding what you need to work on and knowing how to achieve it are two different things. However, there are other ways you might advance your job by establishing positive habits, expanding your network, and getting active in the community.
Make Use of Internet Resources
Detailed information on a wide range of data science topics, both specialist and general, can be found within internet resources. You can increase your knowledge of programming, your foundation in mathematics just by reading internet content.
Online Courses
Online courses empower aspiring data scientists by providing flexible, accessible learning. From business professionals to tech enthusiasts, they offer a convenient path to master crucial skills. These courses are like valuable Businesstoys, offering practical insights and knowledge for immediate application in the data science field.
FAQ's
Embarking on a career in data science requires a strong foundation in mathematics, statistics, and programming. A bachelor's degree in a related field is often a prerequisite, and acquiring additional certifications in data science can enhance your credentials.
Domain knowledge is crucial in data science, as it allows you to contextualize your findings within specific industries. A solid understanding of the domain you're working in enables you to generate more meaningful insights and contribute effectively to business objectives.
Absolutely. Data scientists often specialize in industries such as healthcare, finance, or technology. Specialization allows for a deeper understanding of industry-specific challenges and opportunities, making your contributions more impactful.
Yes, soft skills are essential. Effective communication, teamwork, and adaptability enhance a data scientist's ability to collaborate with cross-functional teams and convey findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Engage in continuous learning through online courses, webinars, and industry conferences. Follow reputable blogs and join online communities to stay informed about the latest tools, techniques, and trends in data science.
Absolutely. Ethical considerations are paramount. Data scientists must uphold principles of fairness, transparency, and privacy, ensuring that their work aligns with ethical standards and legal requirements.


Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *