What is the difference between Data Science, Business Analytics and Big Data
Intro
Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data
Now, how do you define big data?
Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Definition: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Disciplines: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Aims and Objectives: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Application: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Skills and education: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Tools: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Definition: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Operations: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Source of data: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Application: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Skills: Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data
What are the key skills and characteristics of a data scientist?
What are the skills required for a business analyst?
What are Big Data Skills?
Similarities: Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data
Conclusion
Is the concept of data science vs business analytics vs big data confusing you?
Since nowadays these terms are the buzzwords that every business is talking about. Digital business relies on data to understand customer demands, behaviour and purchasing patterns to make informed decisions.
Data is like gold mines for business. They cannot afford to drain money and resources into unachievable goals and objectives.
Therefore, learning about fundamental concepts like data science, business analytics, big data, and machine learning, is important to help businesses in achieving their targets on time.
Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data
Data Science, business analytics, and big data are all various tools and techniques that have been developed to handle high-volume digital data, structured data, unstructured data, and semi-structured business.
In 2008 Jeff Hammerbacher and Dr Patil coined the term “Data Scientist” which means a person who studies Data Science.
Let’s first know what a Data Scientist does.
A Data scientist has immense and deep knowledge of data analysis, scientific techniques, data analysis, artificial intelligence, deep learning, machine learning, data visualisation, and statistics.
A Data Scientist with his knowledge draws data from various sources like media data, web data from sensor data, preprocessing data, images, videos, and sensor data to develop algorithms to develop a data-driven insight and information.
What does Business Analytics do?
In the 19th century, Fedrick Winslow Taylor coined “Business Analytics”, which means a person limited to business operations and business analytics processes. Business Analytics focuses on uplifting the organisation’s business by helping them in making relevant decisions.
Commonly they use tools and techniques like data mining, predictive analysis, and statistical analysis to gain knowledge about the business standard and offer resourceful solutions. In layman's terms, they convert data into insightful information to help businesses in taking important decisions for business development.
Now, how do you define big data?
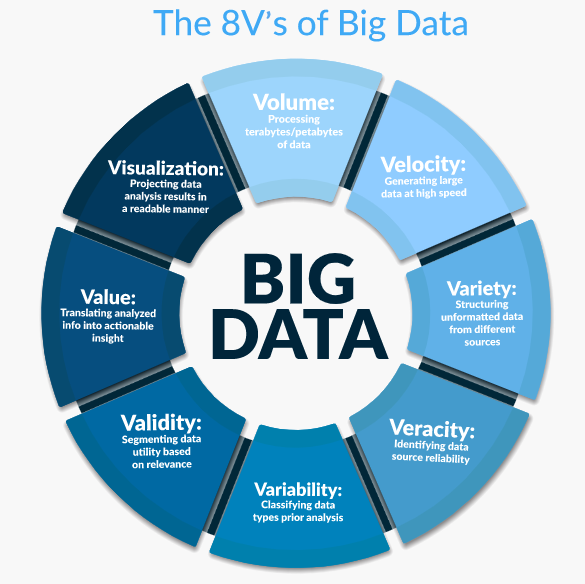
As the name suggests, big data is volumes of data received by the organisation while operating. Data do not have fixed sizes rather they are raw and unstructured. Big Data Analytics analyses and processes such huge data to help businesses in making strategic decisions.
The business receives data from social media, the internet, other organisations, computers, social media and more. Therefore, Big Data is a high velocity that demands innovative measures to turn them into insight for business growth.
Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
If you are a student of Artificial Intelligence, Data Analysis, and Machine Learning, you can begin your career as a Data analyst, data scientist, Machine learning engineer, Business analyst, and Big Data engineer.
Before discussing the differences, the biggest similarity between Data Science and Business Analytics is the achievement of business goals.
Definition: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Data Science focuses on extracting structured, insightful and valuable data from a sea of data to ensure that the data can be used for better application and decision-making for the business.
Whereas, business analytics identifies and anticipates trends and helps businesses to make a data-driven solution. This information and insight from data help businesses to understand the business better.
Disciplines: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Data Science deals with complex and unstructured data and there are huge opportunities under it. The disciplines under Data Science are Machine Learning, Data Engineering, Predictive Analysis, Deep Learning, Statistical Learning, Data Visualisation, Database Management, Data Warehousing, Data Mining, Machine Learning, and Data Analytics.
On the other hand, business analytics is a subfield of Data Science and the disciplines are Business Modelling, Predictive Analysis, Workflow Modelling, Data Mining, Data Analysis, and Statistical Analysis.
Aims and Objectives: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Data Science involves data sourcing, data cleaning, and making data structured so that it can be applied. Business Analytics draws business data to increase revenue. Moreover, data science and business analytics aim at mining data, but their application is different and unique.
Application: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
Data Science is primarily indigent for the business to make insightful decisions, its application is majorly for supporting IT structure and process, developing robotics, and sustaining a good healthy IT infrastructure.
In contrast to that, Business Analytics uses structured data for business operations and helps businesses to earn more revenue and make better decisions.
Skills and education: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
A Data Scientist has to be proficient in data analysis, algorithms, linear algebra, programming, and importantly above all computer science. Additionally, a person should have immense knowledge of statistics, machine learning, and deep learning. However, if the candidate does not have immense knowledge of coding then algorithms and robust processes cannot function.
On the other hand, Business Analysts should have immense knowledge of business planning, analytical skills, storytelling, predictive modelling, and business optimization. Therefore, the major skill required for Business Analytics is to have knowledge of business welfare techniques.
Tools: Difference between Data Science and Business Analytics
In Data Science, one needs sophisticated tools for data modelling are Python, Matlab, Numpy, Pandas, R, PyTorch, Keras, Tensorflow, Sci-kit-learn, SQL, NoSQL, Apache Spark, Jupter, Natural Language Toolkit, and Matplotlib.
In Business Analytics, one needs tools like Microsoft Excel, JIRA, SAS, SQL, Dash, Python, Oracle Analytics Cloud, Tableau, Power BI, and Pencil. Moreover, statics is the sole dependent tool for business analytics.
Difference between Data Science and Big Data
With the growth of the flow of information on the internet, Data Science is becoming quite a challenging area. There is a lot of application of algorithms, programming techniques and intelligent analysis to segregate large volumes of data.
Therefore, big data is an integral part of data science and Data Science and Big Data are inseparable.
Definition: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Data Science focuses on scientific activity and approaches to extract data are always part of Big Data.
In layman's terms, Data Science is a multidisciplinary approach to extracting data. To extract such data scientific methods, programming, advanced analysts, AI, ML, and deep learning are combined to gain insights.
In contrast to that, Big Data involves data that is characterised by huge velocity, variety and volume. It includes various types of data and data types that are generated from multiple sources. For example, big data includes scientific and research data, social media data, stock media data, and sporting event and game data.
Operations: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Data Science analyses data and extracts data from the ocean of data. On the other hand, Big Data is about storing data, and businesses can bring solutions only from processed data sets.
In simple terms, Big Data is about storage, management, and adding PIG, HIVE to the Hadoop framework of data.
Source of data: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
In order to deal with data, Data Science and Big Data sources are different. Data science data are applicable through scientific methods and related to data filtration, preparation and analysis. Moreover, it captures complex patterns and develops models that help in the creation of working apps.
However, Big Data derives its data from users surfing on the internet, electronic devices like RFID, sensors, and online discussion forums. Data generated from system logs are mentioned in spreadsheets, emails, and DB.
Application: Difference between Data Science and Big Data
Every business makes decisions backed up by data, however, the application of Data Science and Big Data is different. Data Science is applicable while internet searches, web development, fraud risks, search recommenders, image recognition, and digital advertisements. Whereas, Big Data is applicable in improving commerce, health, optimising business, telecommunication, security, and research. .
Skills: Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data
In order to handle various forms of data, a data scientist, business analytics and Big Data analytics should possess skills that add a great bonus to your profile.
Furthermore, good knowledge and in-depth understanding of these topics will increase your value in an organisation and offer you a higher competitive edge over others.
Therefore, the questions are -
What are the key skills and characteristics of a data scientist?
- 1. Knowledge of SAS, or R
- 2. Knowledge of coding, especially in Python, Java C, C++, and Perl
- 3. Experience in dealing with HIVE, PIG, and other Hadoop platforms
- 4. Knowledge of SQL database
- 5. Capable of working with unstructured data derived from various platforms like social media, video, and audio.
What are the skills required for a business analyst?
- 1. Knowledge of Statistics, probability, Bayes’ theorem, T-distribution testing, Analysis of variance, Sampling techniques, permutation and combination, and Hypothesis testing
- 2. Knowledge of Python, R, SQLite, MySQL, and Oracle
- 3. Skill Sets on Power BI, Tableau, Qlik Sense
What are Big Data Skills?
- 1. In-depth knowledge of analytical skills for the creation of reports and solutions
- 2. Knowledge of programming languages
- 3. Understanding of business operations and growth.
Similarities: Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data
Data is the primary foundation of and every business needs data for business growth and development. Big Data deals with high volume data, business analytics acquires data and data science aims to uncover patterns of unstructured data.
Conclusion
Data Science, Business Analytics and Big Data share common as well as different frontiers of handling and dealing with data. Moreover, without any of these tools and techniques complex and unstructured data could not be converted into insightful operations.
Which is a good career option: Data Science vs Business Analytics vs Big Data? Data is the future, but which one should you choose for a prosperous future? Therefore, for better understanding and a strong portfolio you need proper guidance that clear all your doubts and offer the best solution to your question.
Check out Business Toy’s Data Science Certification program to learn data science in the most practical way and fast forward your career.



Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *